Hepatology Details

Hepatology is a subspecialty of gastroenterology that focuses on the study, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases and conditions affecting the liver, as well as related organs such as the gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas. Hepatologists are medical specialists trained in managing liver-related disorders, and they deal with a range of issues including:
- Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver, often caused by viral infections such as hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Chronic hepatitis B and C can lead to serious liver damage if left untreated.
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver tissue due to long-term damage, often caused by alcohol abuse, chronic hepatitis, or fatty liver disease. Cirrhosis can lead to liver failure.
- Liver Cancer: Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of primary liver cancer. It is often associated with chronic liver diseases, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- Fatty Liver Disease: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic liver disease are conditions where fat builds up in the liver, potentially leading to inflammation and scarring (steatohepatitis).
- Liver Transplantation: Hepatologists are involved in managing patients before and after liver transplants, including those with end-stage liver disease or liver failure.
- Autoimmune Liver Diseases: Conditions like autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), where the body’s immune system attacks the liver or bile ducts.
- Genetic Liver Disorders: These include hemochromatosis (excessive iron buildup in the liver) and Wilson’s disease (copper accumulation in the liver and other organs).
- Gallbladder and Bile Duct Diseases: Hepatologists also treat conditions such as gallstones, cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts), and bile duct obstructions.
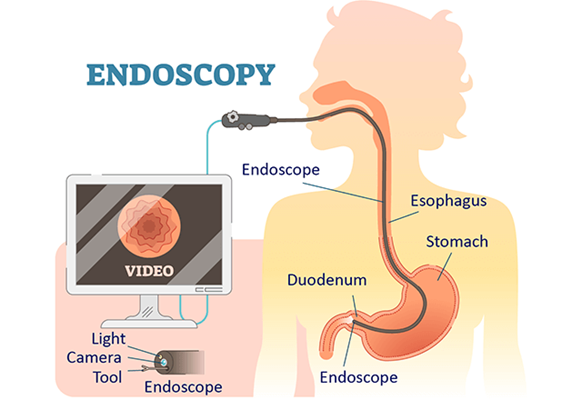
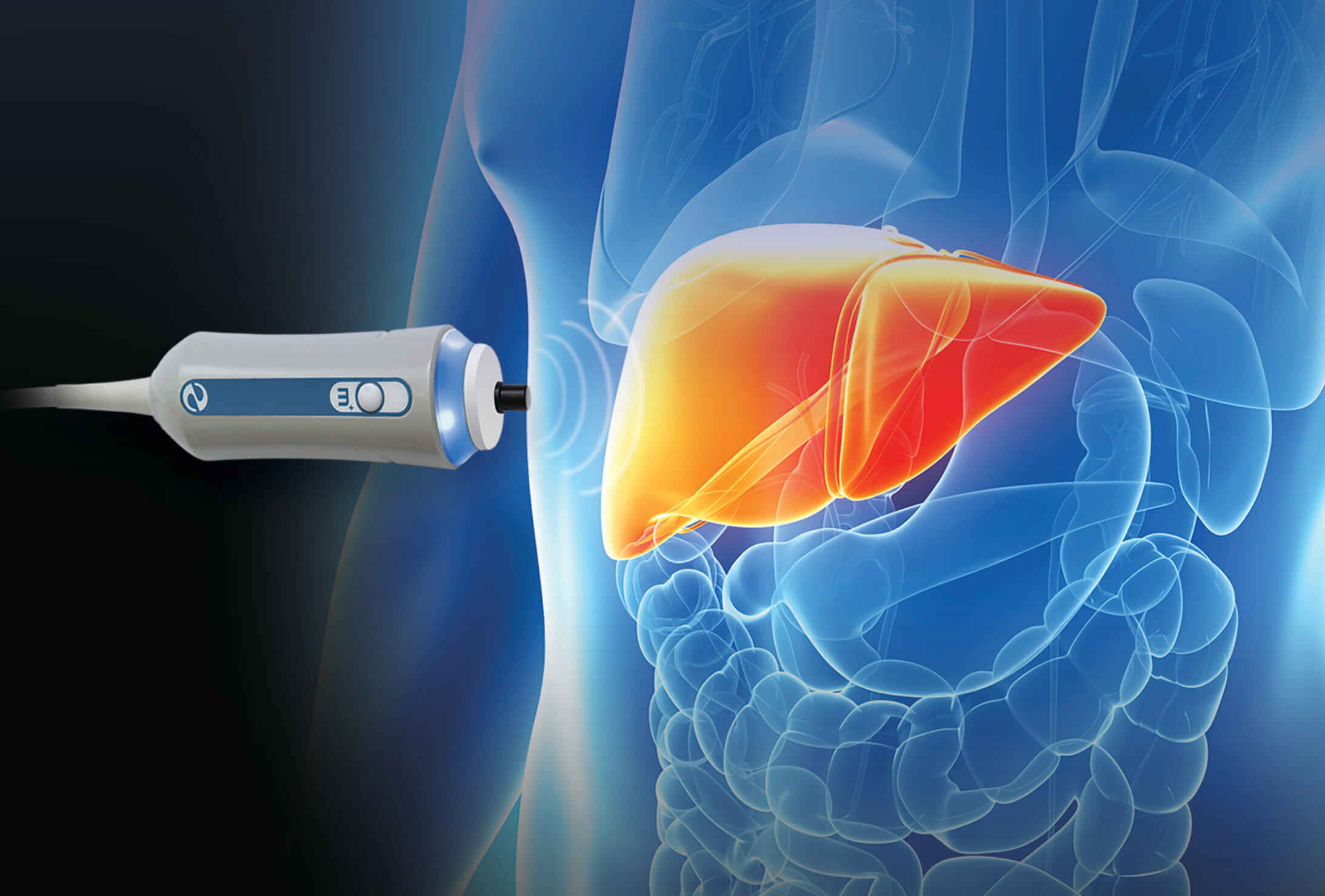
Hepatologists utilize advanced diagnostic techniques such as liver biopsy, imaging (like ultrasound, CT, or MRI), and blood tests to assess liver function and detect abnormalities. In addition, they are involved in managing liver-related complications like portal hypertension and ascites. Treatment plans often include lifestyle changes, medications, or in severe cases, liver surgery or transplantation.